Main Than vs. Then Takeaways:
- Then and than are homophones. This means that they sound almost identical when spoken but have different meanings and spellings.
- When you think of then, think of time.
- When you think of than, think of comparisons.
- Sometimes, than can be used to indicate time, but it is still typically a comparison.
- Then can be an adverb, adjective, or noun.
- Than is a conjunction.
Like affect vs. effect and to vs. too, than vs. then cause a lot of confusion. While many use these homophones interchangeably, they are not the same. Choosing the wrong word may mean that you don’t communicate your message clearly or correctly. In fact, than and then have different functions and meanings. But, there are, of course, some exceptions. Here, we’ll make sure you have everything you need to keep them straight, once and for all.


Then vs. Than Rule
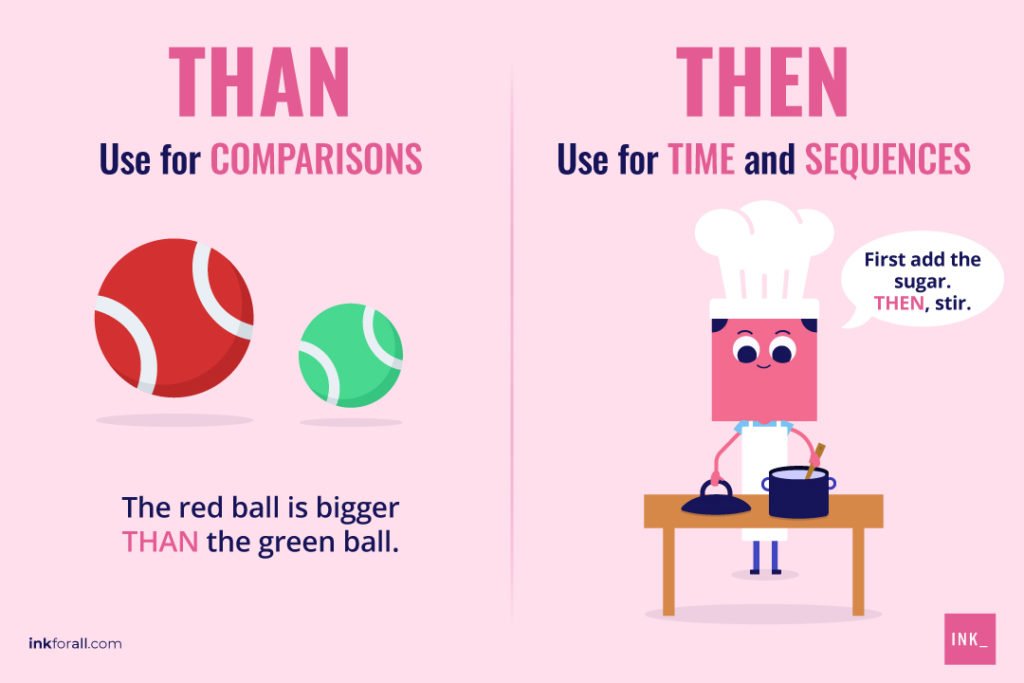
Here’s the best way to tell the difference between then vs. than: associate then with time and than with comparisons. For example, use then for clarifying a sequence of events like writing a recipe or retelling a story (“We went to the supermarket and then headed home.”). Try remembering that the “e” in “then” stands for “events.”
Conversely, use than when making a comparison (“We like going to the smaller shop nearby more than going to the supermarket.”).
You might see then in a comparison, but always about time (“Back then, we were less timid than we are now.”).
Than vs. Then Exception: Comparisons About Time
There is one exception. Sometimes, than can appear in comparisons about time. But in these cases, there is still a comparison involved.
In this example, we’re dealing with time, but it’s secondary. The main function of than here remains the same: to make a comparison.
“He” is comparing his meeting time to 12 pm. He’ll be there no later than noon. In other words, other times are being compared to that one particular time-related target.
This may be confusing because we’re not drawing a 1:1 comparison between two individual things (he arrived earlier than I arrived); instead, we’re comparing one individual thing (12 pm) to a group (all times before 12 pm). Nevertheless, this is ultimately a comparison and as a result, should use then.
What Type of Word is Then?
Then usually refers to time and can function as three types of speech. First, then is usually an adverb (“If you leave, then turn off the lights”). Second, then can be an adjective (“Jackie Kennedy, then Jacqueline Onassis, studied literature“). Finally, it can be a noun (“See you then?” or “We’ll wait until then”). Conversely, than is a conjunction and is for making comparisons (“This cake is sweeter than that brownie”).
How is Then Used in a Sentence?


Then vs.than breaks down to time vs. comparisons. For instance, there are several ways to use then, and they all indicate time. Most often, then is an adverb to help clarify a sequence of events (“Wash then dry the dishes”). What’s more, then helps describe a condition and then a consequence (“If it rains, then we’ll eat inside”). Additionally, then can also be an adjective (“The then CEO”). Finally, then can be a noun (“I’ll see you then!”).
- Clarify a sequence or indicate the order in which certain actions occurred
- Illustrate the relationship between several actions or items
- Illustrate the consequences of a certain action
- Indicate a previously held position
Clarify a Sequence (Adverb)
Describe the Relationship Between a Condition and Consequence (Adverb)
You could also use then to tell the reader when something caused something else to happen. Those examples typically frame the second action as a consequence of the first. In that case, you’ll probably use an if/then construction, making it clear the connection between the two actions.
Indicate a Previously Held Position (Adjective)
Remember, then can be an adjective, an adverb, or a noun. It’s most often used in sentences that are discussing time. You might be demonstrating a series of events, indicating a relationship between several actions.
Refer to Past or Future Time (Noun)
How is Than Used in a Sentence?
Than is a conjunction used for comparisons (“She is taller than I am”).However, then is an adverb, adjective, or noun related to time. A point of overlap is that than can appear in comparisons about time (“Please arrive no later than 9 a.m.”).
Overall, than is important because it helps enrich the level of clarity and detail in your writing.
When the relationship between the nouns, verbs, and adjectives in a sentence isn’t equal, you can use than to indicate that one takes precedence. This helps clarify status, physical stature, order of operations, and other important information.
Than helps us understand which is bigger, better, louder, or simply more favored. For example, using “than” is a good way to paint a picture of how items contrast each other.

Here are easy examples of how to use than vs. then in a sentence:
How to use Less Than and More Than
How to use More Than in a Sentence
How to Use Less Than in a Sentence
Common Expressions: Than vs. Then
Is it Other Than or Other Then?
The correct phrase is “other than” and not “other then.” Use “other than” to indicate an exception (“Other than cats, she’s not a fan of animals”). The item or situation that comes directly after “other than” is the only example mentioned that doesn’t fit into the described scenario. In this way, this structure compares the exception to the rule. Therefore, “other than” expresses a comparison. Since we use than for comparisons and then for time, “other then” doesn’t make sense here.
Is it Well Then or Well Than?
The correct phrase is “well then“, not “well than.” Use the phrase well then to switch topics. Similarly, use this phrase to start concluding a conversation or saying goodbye (Well then, I have to go. See you tomorrow!). Moreover, if a person says something strange or interesting, the response well then indicates that you’re surprised and unsure of what else to say. For this reason, some use it sarcastically.


For instance, say your friend has a history of jumping and hitting their head. You might ask them whether they think that’s a good idea. When they reluctantly say, No…, you could respond with, Well then….?! to suggest they should know better.
Notice that because “well” is an interjection in these examples, there’s often a comma between “well” and “then.”
Is it Rather Than or Rather Then?
The correct phrase is “rather than“, not “rather then.” This is because than is most commonly used in comparisons (“He’s taller than her”) while then is more for discussing time (“Sal went to the store then stopped by the post office”). Since “rather than” compares two actions or choices, it only makes sense to use “rather than” instead of “rather then.”
Is it Older Than or Older Then?
Both “older than” and “older then” are correct. But, they are not interchangeable because they mean different things. Usually, we use then for time and than for comparisons. However, this question is confusing because both “older than” and “older then” deal with time and comparisons, but in different ways. Use “older than” to compare the age of one person to that of another person (“My sister is older than I am”). On the other hand, we use “older then” to refer to a time other than the present (“See you then!” Let’s wait a week and buy it then”).
Technically both options are correct. Which one you choose to use depends on your message and the surrounding context.
Rather than accidentally making a mistake with then or than in the future, bookmark this page and review as needed. Happy writing!
Is it Better Than or Better Then?
The answer will depend on the context of your statement. If you’re comparing two things in your sentence, then the correct phrase is “better than.” However, if you are referring to a certain time in the past as better, then “better then” is the right phrase. See examples below:
Let’s see if Then and Than Still Confuse you
Then vs Than Question #1

The answer is C. “Then” suggests the order in which specific actions occurred, while “than” is used for comparison.
Then and Than Question #2


The answer is TRUE. Although both words sound alike, they have different meanings.
Than Question #3

The answer is BOTH. “Than” is a conjunction or preposition, depending on how it is used in a sentence.
Than or Then Question #4

The answer is THAN. “Than” is commonly used in comparisons.
Then or Than Question #5


The answer is THEN. “Then” is used to indicate time.
Then vs Than Question #6


The answer is THAN. “Rather than” compares two actions or choices, with the person in question opting for one over the other.







I thought it was other then not other than
Hi, Tammy! You’re definitely not the only one. “Then” and “than” practically sound the same, but only “than” makes sense here because you’re making a comparison. I’m glad our article helped clarify this one! Thanks again for reading and for taking the time to comment. Best!
I was very confused at first, but then i started to understand. Thanks!
Hi Kinsley!
We’re glad that our article has helped clear your confusion about the use of “than” and “then”. Have you seen our article on “while” and “whilst”? You might find that one interesting as well.
Rechelle