You have a burning question. You need it answered now.
You type the question in the Google search bar. Within seconds, you have hundreds of websites and posts literally lining up to be the best answer to your question.
But how does Google decide which piece of content deserves to answer your question first? How does Google rank content to filter the best matches for your search.
While the specific mechanics of Google’s RankBrain algorithms are still a bit of a black box, we have an idea of how RankBrain reads, understands, and ranks content. We call it the Rank Candidate Theory (RCT) and it goes a little something like this…
What is the Rank Candidate Theory?
The Rank Candidate Theory is the idea that Google crawls your page, scrapes your content, and determines from a deep understanding of the content if you meet the user’s intent. If you do, Google considers your page a rank candidate. As a result, it directs some traffic to your page to test user satisfaction. If users like your page, your rankings will go up.
Content relevance and user experience will, therefore, become increasingly important ranking factors.
In short, Google reads your page and decides if it is good enough to answer your query. If your page seems like a relevant candidate, Google will send some traffic your way as a test.
In this way, Google is like a match-maker. It listens to you and works to understand what you want. Then, it looks for options that match what you’re looking for and filters them into a list of candidates.

It sends you on a first date with them to see if you’re compatible. If you’ve found everything you were looking for in that candidate and enjoyed your first date, it’s a match made in heaven.
In 2016, we founded Edgy Labs to validate the Rank Candidate Theory 1.0.
Rank Candidate Theory Background
Google is now able to read a page just like a person does. But, it didn’t get there overnight.
Let’s rewind to 2012 when Google was first able to detect cats in YouTube videos. Then, in 2014, Facebook made news when they announced they were able to recognize faces with 97.35% accuracy using DeepFace4.
These two technological breakthroughs were like a flashing neon sign that the world of internet marketing was about to change forever.


The industry was inevitably moving toward neural networks. Global ranking factors as we knew them were about to be killed off.
The nail in the keyword stuffing coffin? Google would begin using their neural network advances for search engine optimization (SEO).
So, in 2016, we set out to test the hypothesis that would become the Rank Candidate Theory developed by INK Co. CTO, Alexander De Ridder.
Putting the Rank Candidate Theory to the Test
Our first priority in testing the rank candidate theory was purchasing a brand new domain, edgylabs.com.
Being a brand-new site, it had no domain authority. The goal was to optimize this fresh-faced site for technical SEO and publish content.
Also, the key to testing our theory was to not influence our experimental content with link building strategies.
Using this method, we were able to test how Google responded to different content optimization strategies. And, different types of content.
By the sheer power of content optimization, we organically grew a brand-new domain to 100,000+ monthly sessions — all from a cold start.
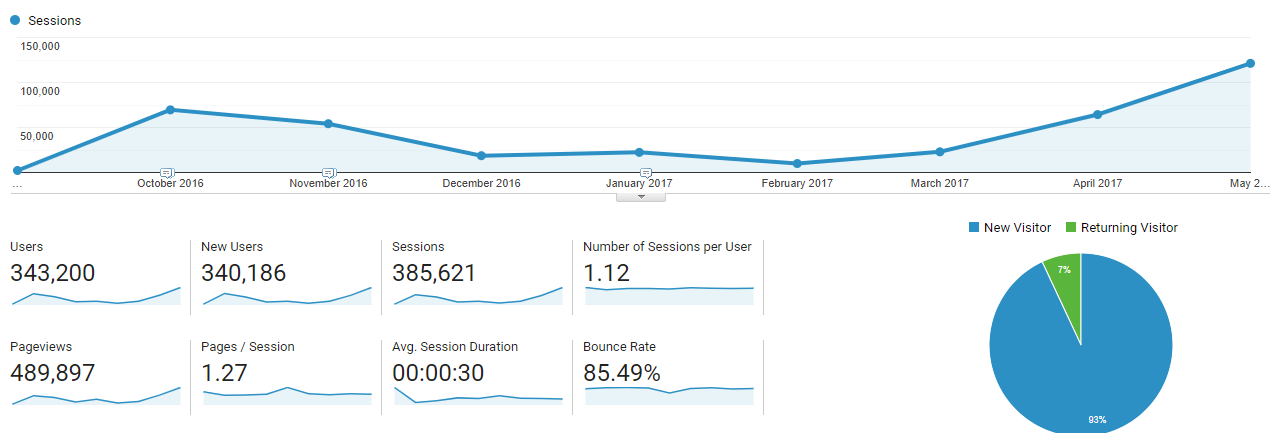

The above chart helps illustrate how content relevance was a new “page authority” signal, capable of outperforming the link-based rank approaches of the past.
Rank Candidate Theory Test Results
1. Relevancy is King
First, we noticed that content will be tested by Google with some traffic. This occurs even if the content lacks backlinks and comes from a site with little domain authority, provided the site has decent technical optimization.
The decisive factor? The content must match the searcher’s intent by completely answering the query searched. In short, the content must be relevant to what you search and must be the best answer out there on the topic.
In practical terms, this is exactly the reason why many pieces of content fail at becoming a Rank Candidate; they just don’t do a great job of meeting the searcher’s expectations.


They just aren’t as relevant or as comprehensive as they need to be. As a result, these sites aren’t prioritized in SERP.
2. Google Sends Test Traffic
Typically, the next step after identifying a relevant candidate would be for Google to send a trickle of traffic to the candidate page.
Then, Google subsequently either stops sending traffic to the candidate page or sends a lot of traffic.
It’s in this period of time where that Google is testing to see how satisfied users are with the answer that the candidate page provides.
Just like a first date, the more engaging, comprehensive, and relevant the content, the better the final outcome. This is what we understand as “RankBrain activity”.
In other words, AI decides if you are worthy of a chance. But RankBrain uses actual users to contribute to the ranking data. This, in turn, helps further the decision of where your page will end up ranking.
Bottom Line
Worry about how to become a Rank Candidate by making your content the best resource available on the subject. Then, ensure that the content achieves good engagement metrics with its target audience.
How Do You Know If Your Content Is the Best?
Ranking is a competitive process. Therefore, understanding what your content is up against is paramount.
We developed and tested our Rank Candidate Theory over the course of two years. During this time, we learned how to do these kinds of competitive analyses.
The process involved studying which pages were already ranking for a certain keyword or intent group. Then, we identified all of the ingredients that made the top pages the best resource on the subject.
Basically, we watch Google and picked its (Rank)Brain.
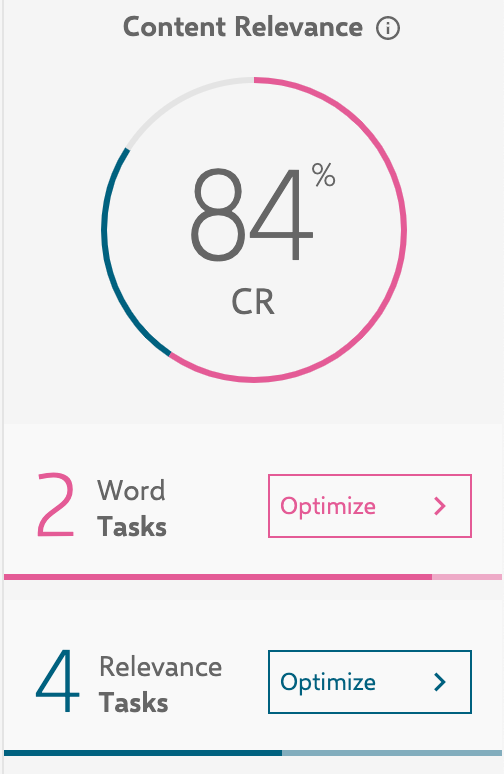

Once we had a baseline of what defined “the best”, we set out to craft a piece of content that beat it.
After much research, we realized that practically all SEO apps and content optimization tools were still using a rules-based approach to content recommendations. None of them accounted for this crucial analysis of the competition.
Like RankBrain, we realized that content optimization in itself is a black box for most writers out there. We know how many hours go into crafting a post or creating content.
And, we know how frustrating it is when all of that hard work does get seen by the people you’re writing it for.


We discovered that 55% of marketers say content creation is their top inbound marketing priority, but over 90% of web content will never be read.
So, we decided to take all of those years of research and our Rank Candidate Theory and put them into designing a next-generation Content Performance Optimization (CPO) platform. Our objective is to help content writers take control of their own search destiny.
We developed the AI-enabled INK platform. We designed it based on our Rank Candidate Theory principles:
- Optimize the content’s chances to qualify as a rank candidate with Google by ensuring it is the most relevant resource on the topic
- Optimize the content’s language to improve user satisfaction by ensuring it is written precisely for the target audience.
Start typing in INK. Just like Google, the INK platform reads your work as you write and compares it to similar content online, in real-time.
It comes back with a Content Relevance Score which lets you know how relevant your content is to the topic or keyword you’re targeting and gives suggestions on how to increase relevancy.
To learn more about the science that powers INK and more about the Rank Candidate Theory, check out my white paper on the subject and play around with INK. It’s free. We made it for you. Put our Rank Candidate Theory to the test. How high can your content rank!

