Main Prepositional Phrase Takeaways:
- Prepositional phrases help show the relationships between the nouns, pronouns, and other supporting words in a sentence.
- Prepositional phrases contain a preposition, an object, and sometimes one or more modifiers.
- There are two types of prepositional phrases: adverbial and adjectival.
- “Before I leave,” is an example of an adverbial prepositional phrase.
- “The sandwich on the table” is an example of an adjectival prepositional phrase.
- Simple prepositions are just one word.
- Complex prepositions contain two or more words.
- Some words can be both adverbs and prepositions. Prepositions always relate to an object.
Prepositional phrases give your content power. Instead of simple, drab sentences that lack color, you can create an entire world of detail. Here’s a look at prepositional phrases, how they work, and the best way to use them.


What Is a Preposition?
Before we start discussing prepositional phrases, let’s first define what a preposition is. Prepositions are words that show the relationships between words in sentences. They usually come before nouns, pronouns, gerunds, or clauses to show place, location, time, and direction or introduce an object in a sentence. For example:
On, near, over, since, and under are all prepositions. These words allow readers to visualize where an object is located or when something happened. If you want to know more about prepositions, feel free to check our article 5 Types of Prepositions: An Easy Guide. Now, moving on to our main topic, what is a prepositional phrase?
What Is a Prepositional Phrase?
A prepositional phrase is a group of words composed of a preposition, an object (noun or pronoun), and the word that modifies the object. Prepositional phrases function as information-givers in a sentence. Let’s take this sentence as an example: “With a sharp knife in hand, the man freed the dog from its leash.” “With” is the preposition, “knife” is the object, and “sharp” is the word that modifies the object. Together as a prepositional phrase, it tells the readers what the man used to free the dog off its leash.
In most cases, writers use a prepositional phrase to modify a verb or a noun.
For example, why say “you went out” when you can say that “you went out to an incredible party?”
Then, you have the option to add a modifier.
“A bit” modifies or further describes the time of departure.
How Do You Identify a Prepositional Phrase?
A prepositional phrase starts with a preposition and ends with an object, which could be a noun, pronoun, gerund, or clause. The object at the end of the prepositional phrase is referred to as the “object of the preposition.” For you to easily identify a prepositional phrase, you need to know the format or pattern it follows in a sentence. There are two ways to write a prepositional phrase, as illustrated below:
Preposition + Object (Noun, Pronoun, Gerund, or Clause)
Here are some examples of prepositional phrases following the preposition + modifier + object format:
Now, the following are examples of prepositional phrases written in the preposition + object format:
If you can spot any of these two patterns, you’ll be able to identify prepositional phrases easily in any sentence.

What Is an Example Of a Prepositional Phrase?
Here are some examples of prepositional phrases in action. We’ll give you a sentence, identify the prepositional phrase, and explain how it works.
Here, we’re demonstrating the connection between the rainbow and where the Wicked Witch lives.
How are the couch and magazine related? One fell behind the other!
Why did Eliza jump? “For joy!”
“By the elevator” indicates where the room is.
Types Of Prepositional Phrases
There are two types of prepositional phrases, depending on the modifier describing the object: adverbial and adjectival. Adverbial prepositional phrases function as adverbs and answer questions like where, when, how, and why. Adjectival prepositional phrases act as adjectives and answer one of these two questions: What kind of?Which one?
In the succeeding sections, we’ll discuss the major differences and effective usage of these two types of prepositional phrases.
What Is an Adverbial PrepositionalPhrase Example?
Adverbial clauses get their name from the fact that they function as adverbs.
For example, we use adverbial prepositional phrases to show timing or cause and effect. They might tell you when or where something happened. They might also detail how something happened or to what extent.
In this example, “because I went to the store early” is an adverbial clause. This is because it demonstrates how the action in the second part of the sentence came to be.
“Before it sold out” is also an adverbial phrase because it described when that action took place.
Here, “Since Marika left her wallet at home” demonstrates what caused her to have to borrow money.
What Is an Adjectival Prepositional Phrase Example?
On the other hand, an adjective phrase modifies the noun or pronoun that comes immediately before it.
“On the island” describes the man. The object of the prepositional phrase is the island. What’s more, the phrase itself indicates how the island and the man are connected.
In this case, the pantry is the object, and the prepositional phrase is describing the link between the cake and its location.


Prepositions That Begin Prepositional Phrases
Here are some examples of common prepositions that you often see at the start of prepositional phrases. Jump over to our types of prepositions guide to explore a full list of common, simple and complex prepositions.
| Aboard | About | Above | Across | After |
| Against | Along | Amid | Among | Around |
| As | At | Before | Behind | Below |
| Besides | Between | Beyond | But | By |
| Concerning | Considering | Despite | Down | During |
| Except | Excluding | Following | For | From |
| In | Inside | Into | Like | Minus |
| Near | Of | Off | On | Opposite |
| Outside | Over | Past | Plus | Regarding |
| Round | Save | Since | Than | Through |
| To | Toward | Under | Underneath | Unlike |
| Until | Up | Upon | Versus | With |
There are also some multi-word prepositions. These contain two or more words that function together to create a complex preposition.
- According to
- In spite of
- Along with
- On account of
Can You Begin a Sentence With a Prepositional Phrase?
The quick answer to this question is YES. You can begin a sentence with a prepositional phrase. Prepositional phrases appearing at the beginning of sentences are called introductory prepositional phrases. Besides giving additional information, introductory prepositional phrases also help provide a sense of flow to any written work. They make the text less choppy and pleasurable to read. Read the following paragraph:
“Since 1985, the coffee shop across the street has served thousands of locals and tourists. It’s a favorite spot for travelers and people who want to grab a quick cup of coffee before starting their busy day. Beside the famous coffee shop, you’ll find the town’s only souvenir store where you can buy all sorts of locally made products.”
The ones underlined in the paragraph above are introductory prepositional phrases. Notice how they provide extra information and help with the flow of the sentences? Now, you also need to pay attention to the placement of your comma when using introductory prepositional phrases.
Comma After a Prepositional Phrase
As a general rule, you can choose to use a comma after a short introductory prepositional phrase or forego using one. By “short,” we mean prepositional phrases that are no longer than four words. Prepositional phrases longer than four words automatically get a comma after them. For example:
Is It a Preposition or an Adverb?
Some words can function as prepositions and as adverbs. You can easily figure out whether a word is acting as a preposition or an adverb by looking for the object.
- If your word refers to an object, it’s probably a preposition.
- If your word doesn’t refer to an object, or there is no object in sight, it’s probably an adverb.
In the first sentence, “up” doesn’t refer to anything. There is not object. Therefore, “up” is acting as an adverb here.
However, in the second example, “up” does refer to an object. For example, “up” is followed by a noun (the hill). As a result, it’s a preposition in this case.
You can confirm that “up” is a preposition here by asking and answering this question: Where did she run? She ran up the hill!
Here’s another one:
In the first example, all we know is that Clark walked across something. We don’t know what that something is, because there is no object. Consequently, “across” is an adverb here.
In the second example, we find out that Clark walked across a courtyard. Since “courtyard” is the object, and across becomes a preposition.


Quick Prepositional Phrase Grammar Quiz
Prepositional Phrase Question #1


The answer is A. Under the bed shows the relationship between the monster and the whispers.
Prepositional Phrase Question #2
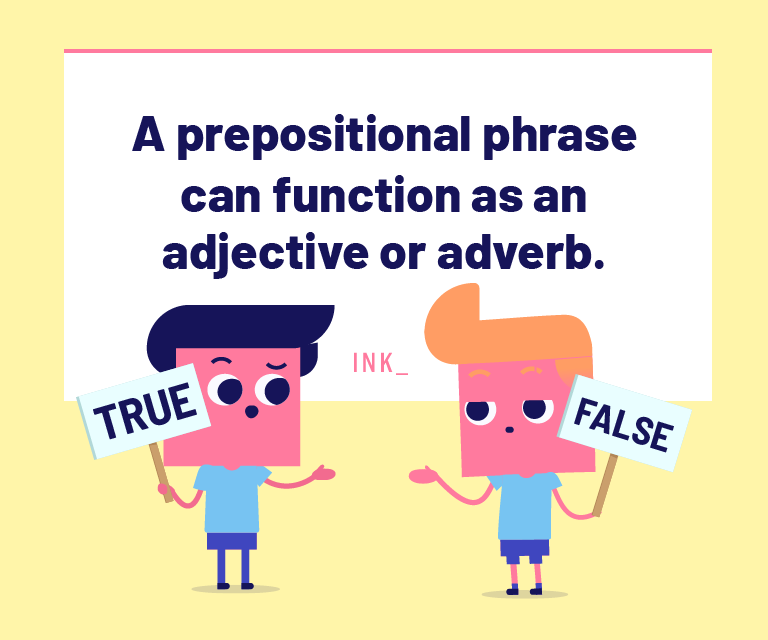

The answer is TRUE. Prepositional phrases can function as either adjective phrases or adverb phrases to modify other words in a sentence. For example, "The girl with him is his daughter."
Prepositional Phrase Question #3


The answer is C. A prepositional phrase must include a preposition, its object, and any modifiers of the object.
Prepositional Phrase Question #4


The answer is C. The object of the preposition can either be a noun or a pronoun.


Written by heart !!
Hi, Saurabhn! Thank you for reading. We definitely put our heart, soul, and a lot of research into these pieces. I’m happy you found it valuable. Take care!
Thank you for this useful post.. Could you please write about functions of prepositional phrase and structure of prepositional phrase?
Hello Dinantha! Thank you for the positive feedback and we’re glad that you find our article helpful. Regarding your request, it’s already discussed in this post. Please check the section titled “How Do You Identify a Prepositional Phrase?” Have a great day!